SimNano energy minimizer
Description:
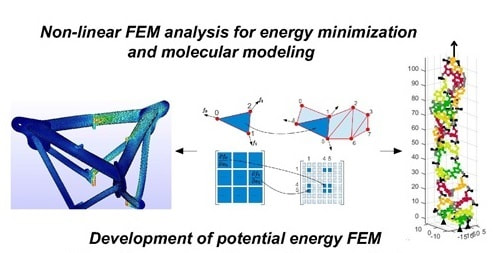
SimNano is an simulation platform that is equipped with a new energy minimization algorithm, that achieves excellent convergence properties and is also computationally highly efficient; therefore, becomes suitable for dealing with large-scale molecular systems. SimNano relies on the analytical calculation of gradient vectors and hessian matrices of the molecular systems by applying a simulation method inspired from structural mechanics and the finite element method (J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56 (10), 1963-1978). The core of the proposed minimization algorithm is an approximate trust region preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm suitable for dealing with large-scale optimization problem along with the implementation of specialized treatment of the data structure that take advantage of the sparsity of the hessian matrices. The later ones are beneficial and often rather necessary, improving speed and memory requirements. Several test cases are examined and the results are compared with those obtained by a popular molecular simulations software (Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator-LAMMPS). The comparative results indicate that the proposed method has superior convergence properties to those of the algorithms that generally are employed in the field (i.e. nonlinear conjugate gradient, BFGS, algorithms etc.). The complete SimNano (x86, x64) simulation platform can be downloaded, enabling researchers in the field to build molecular systems and perform energy minimization runs.
SimNano is an simulation platform that is equipped with a new energy minimization algorithm, that achieves excellent convergence properties and is also computationally highly efficient; therefore, becomes suitable for dealing with large-scale molecular systems. SimNano relies on the analytical calculation of gradient vectors and hessian matrices of the molecular systems by applying a simulation method inspired from structural mechanics and the finite element method (J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56 (10), 1963-1978). The core of the proposed minimization algorithm is an approximate trust region preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm suitable for dealing with large-scale optimization problem along with the implementation of specialized treatment of the data structure that take advantage of the sparsity of the hessian matrices. The later ones are beneficial and often rather necessary, improving speed and memory requirements. Several test cases are examined and the results are compared with those obtained by a popular molecular simulations software (Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator-LAMMPS). The comparative results indicate that the proposed method has superior convergence properties to those of the algorithms that generally are employed in the field (i.e. nonlinear conjugate gradient, BFGS, algorithms etc.). The complete SimNano (x86, x64) simulation platform can be downloaded, enabling researchers in the field to build molecular systems and perform energy minimization runs.