Projects:
|
Spin-dependent Transport in Nanostructures |
|
|
|
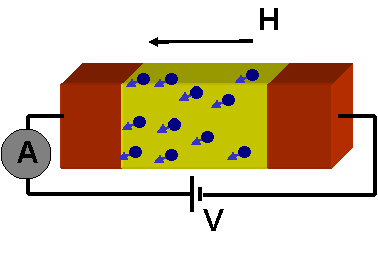
Project Summary The aim of the project is to investigate the correlation between magnetic configuration and electronic conductance in assemblies of magnetic nanoparticles in order to reveal the factors that determine the value of the Giant Magnetoresistance effect and the its sensitivity to the applied field. We study granular systems where the transport mechanism is diffusive and nanoparticle assemblies in insulating matrix (self-assembled systems) where the transport mechanism is phonon-assisted hopping. The theoretical tools we use is the Green function Kubo formalism to study diffusive (metallic) systems and the Resistor Network Models to study hopping transport. The underlying micromagnetic configuration is obtained by Monte Carlo techniques.
|
|
Review article on our work - A review article on the magnetic and transport properties of nanoparticle assemblies with random morphology. |
|
Selected Publications |
|
D. Kechrakos and K. N. Trohidou, Phys. Rev. B 71(5) 054416 (2005) |
|
D. Kechrakos and K.N. Trohidou, Conditions for optimum giant magnetoresistance in granular metals, J. Appl. Phys. 89 7293-7295 (2001) |
|
D. Kechrakos, K.N. Trohidou and J. A. Blackman, Scaling behavior of the giant magnetoresistance of magnetic aggregates, Phys. Rev. B 63, 134422 (2001) |
|
D. Kechrakos and K. N. Trohidou, Phys.Rev. B 62 3941-3951 (2000) |