| |
|
Research Interests
HexaTerra
Electrohydraulic Servosystem |
| 
|
|
The
HexaTerra servomechanism is an eighteen-dof electrohydraulic system.
The major goal of the research was the development of a modular
"stepping locomotion" system for installation on subsea
trenching machines used for subsea energy cable burial. |
Optimum
Design of Electrohydraulic Servosystems |
| 
|
|
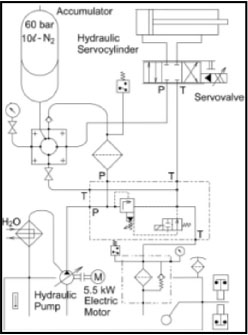
An
optimal hydraulic component selection for electrohydraulic systems
used in high performance servo tasks. A systematic methodology
for the generalized selection of electrohydraulic servo-systems
components is developed. This is achieved using a programming
code, which takes into account the servosystem dynamics and an
optimization algorithm minimizing a task-related objective function.
Three optimization criteria are considered; namely, the minimization
of the required hydraulic supply power, of the total weight and
of the total cost. A detailed scalar set of component databases
is employed, which includes data related to key hydraulic components,
such as cylinders, servovalves, accumulators, electric motors
etc. The databases consist of records with real industrial data. |
Six-dof
Electrohydraulically Driven Stewart Platform |
| 
|
|
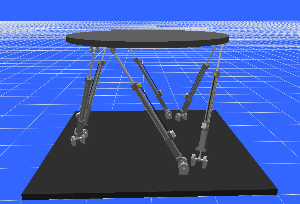
The
Stewart servomechanism is a six dof closed kinematic chain mechanism
consisting of a fixed base and a movable platform with six linear
actuators supporting it. Rigid body and electrohydraulic models,
including servovalve models are employed and described by a set
of integrated system equations. Friction and leakages of hydraulic
elements are also included. Model-based control schemes of the
full electrohydraulic servosystem have developed, which they use
the system dynamic and hydraulic model to compute servovalve currents
in analytical form. The proposed methodologies can be extended
to electrohydraulic serial manipulators and simulators. |
Single-dof
Electrohydraulic Servosystem |
| 
|
|
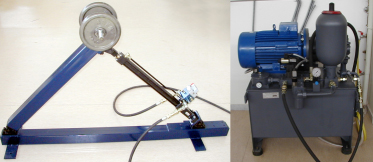
The
major goal of the research was to develop, test and design new
control laws for electrohydraulic servos. The control schemes
were based on accurate dynamic and hydraulic modelling all of
the system elements, emphasizing new methodologies of servovalve
modelling. Parameter identification algorithms were developed
in order to find system parameters. These servosystems functioned
under real-time OS (QNX). Optimization methods with power, weight
and total cost criteria of such servosystems have been developed. |
Sarcos
Master-Slave Telerobotic System |
| 
|
|
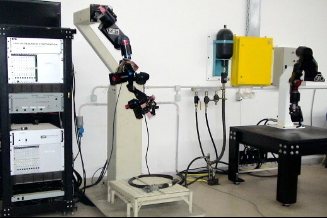
The
Sarcos Electrohydraulic Dexterous Teleoperation System is consisted
of two ten-dof robotic manipulators, i.e. master and slave, which
are designed to emulate the human arm. The major goal of the research
is to develop, test and design new control laws for the slave
arm. The control schemes are based on accurate dynamic and hydraulic
modelling all of the system elements, emphasizing new methodologies
of servovalve modelling. Parameter identification algorithms are
developed in order to find system parameters. These servosystems
will be functioned under real-time OS. |
|

